Materials Used in Palisade Fences
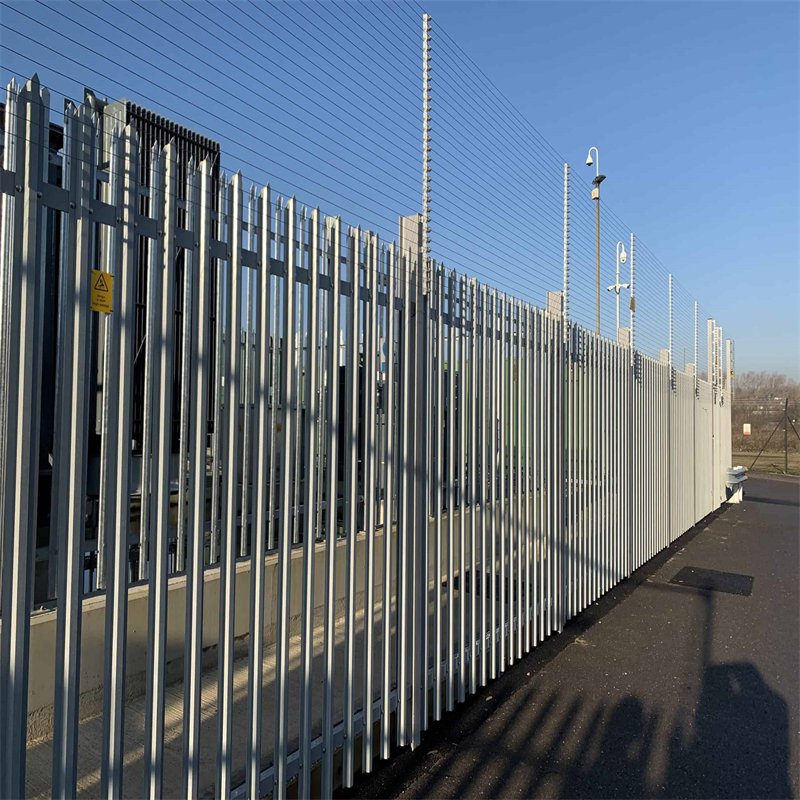
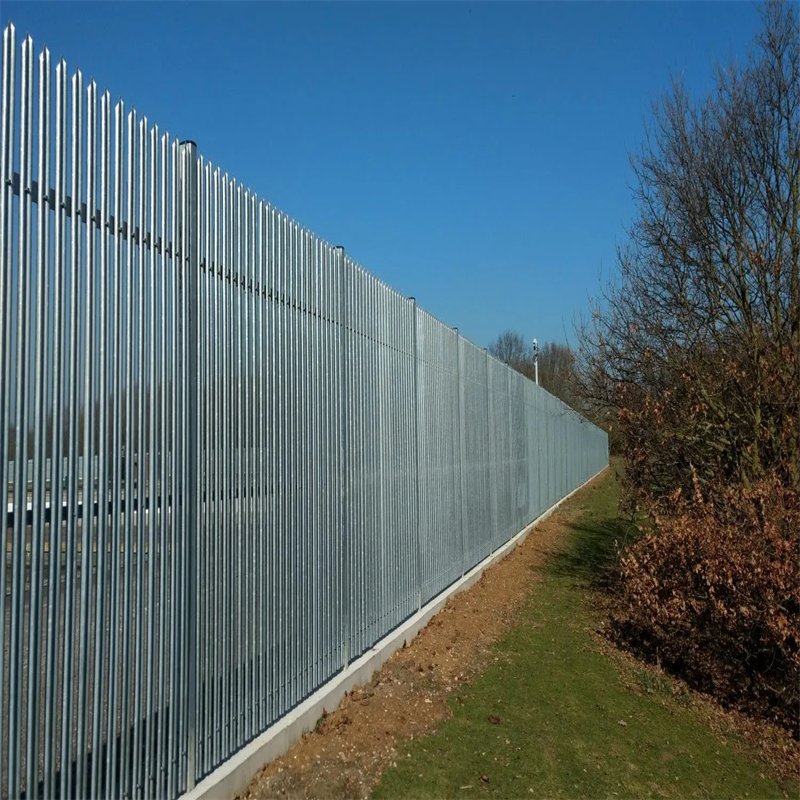
<p>Palisade fences are primarily constructed from galvanized steel and PVC-coated steel. The hot-dipped galvanized steel variant is favored for its thicker zinc coating, which offers superior corrosion and rust resistance, ensuring durability and longevity. This type of fence stands up well against the elements, making it a practical choice for long-term use.Alternatively, PVC-coated palisade fences provide exceptional corrosion and rust resistance while also offering an array of color options to harmonize with different environments. Popular colors include green, blue, yellow, and white, but the fences can also be customized in single or mixed color schemes to suit specific aesthetic preferences.

PF-01: Galvanized palisade fence. |

PF-02: PVC coated palisade fence. |

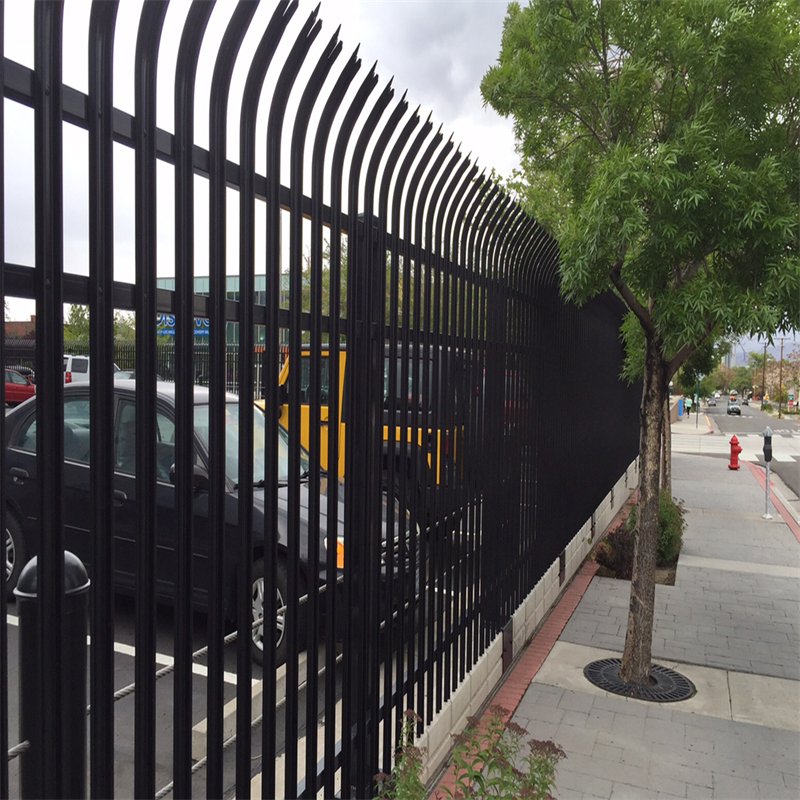
PF-03: General palisade fence for garden security. |

PF-04: Security palisade fence for residence protection. |
Components of a Palisade Fence
A palisade fence consists of several essential components: pales, rails, posts, stays, and various accessories that all work together to boost its structural integrity and functionality.
Pales
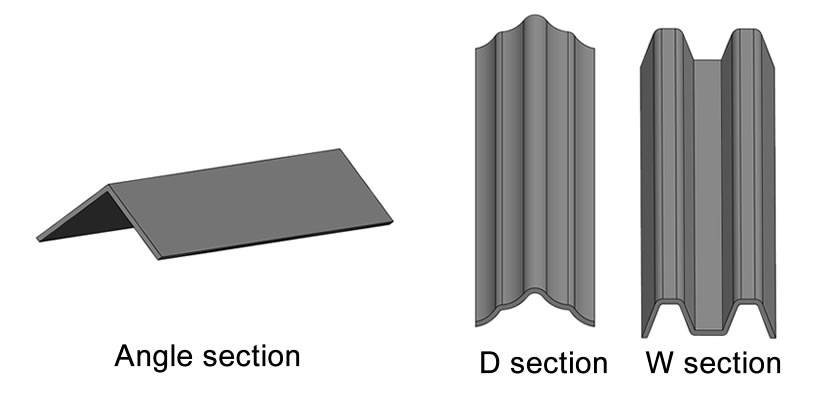
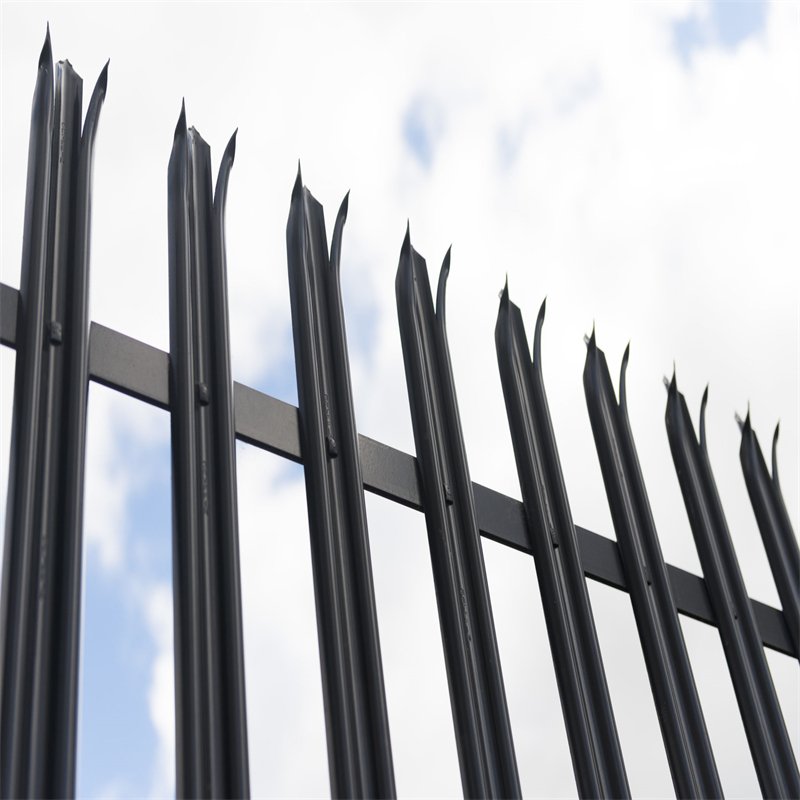
Pales form the primary element of the palisade fence, crafted through hot or cold forming processes. These are available in designs suitable for general purposes as well as for enhanced security needs. General-purpose pales might be corrugated or shaped into angle sections, while security pales feature corrugation with fastener head protection to prevent tampering. Manufacturers create pales with a length tolerance of ±2 mm, ensuring uniformity across the fence.
Types of Palisade Fence Pales
- Corrugated Pales:
- W Type: Renowned for their durability and resistance to vandalism, W section pales suit high-security requirements. Installers attach these to horizontal rails using short bolts that ensure a tight, secure fit, providing maximum protection.
- D Type: For areas requiring medium security, such as boundaries, installers use D type pales. They attach these with long bolts to strike a balance between security and resistance to damage.
- Angle Steel Pales:
- Suitable for general security needs, installers either bolt or weld these pales to the horizontal rails. They are a popular choice in residential areas where security effectiveness needs to blend with aesthetic appeal.
PF-05: Various Palisade Fence Pale Designs
Palisade Fence Pale Head Types
Palisade fence pales come in various head types, with each style offering unique security features. Both corrugated and angle pales have distinct designs that enhance the security of the entire system and help prevent intruders from climbing over. These specialized head types are crucial in fortifying the fence against breaches, making it more difficult for potential intruders to gain access to protected areas.
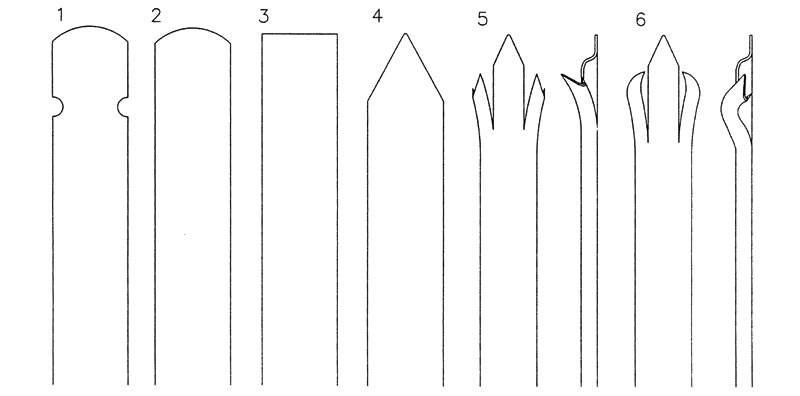
PF-08: Six types of corrugated pale head.
Corrugated pale head types are as follows:
- Round and notched type.
- Round only type.
- Plain type.
- Single pointed type.
- Triple pointed and splayed.
- Triple pointed, splayed and returned.
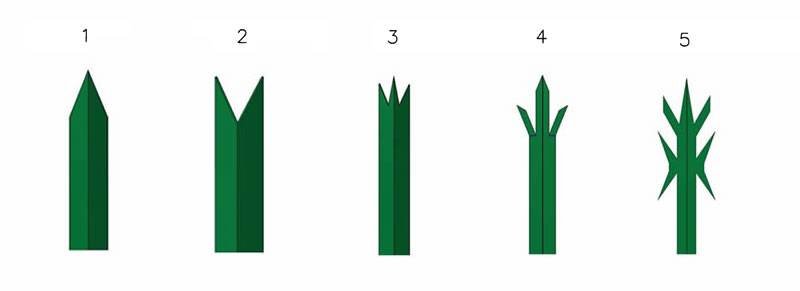
PF-09: Five types of angle pales head.
The angle pale head types are as follows:
- One pointed.
- Double pointed.
- Triple pointed.
- Triple pointed & sprayed.
- Seven spikes.
Types of Fixing for Palisade Pales
Palisade pales connect to the rails at each intersection using various methods, ensuring strong security and stability:
Welding: Workers weld the pales to the rails with 3 mm fillet welds, each weld at least 30 mm long on either side of the pale. All welding follows BS RN 1011-1 and BS EN 1011-2 standards, performed by personnel certified under BS EN 287-1 to ensure the welds are high-quality and durable.
Bolting: For this method, workers use bolts at least 8 mm in diameter to secure the pales to the rails. The design of the bolt heads minimizes protrusion from the pale surface to lower the risk of tampering and remove potential footholds.
Riveting: Riveting is another strong method for attaching pales to rails, similar to bolting. Rivets used also measure at least 8 mm in diameter. The rivet heads, like bolt heads, protrude minimally to discourage tampering and keep the surface smooth.
Both bolting and riveting methods aim to boost the fence's security features. In Security Pale (SP) designs, the fastener heads are specially shielded to resist tampering and withstand external forces, thus boosting the overall security of the palisade fence.

PF-06: W pale palisade fence. |

PF-07: D pale palisade fence. |

PF-10: Bolting type. |

PF-11: Welding type. |
PF-12: Riveting type.
Understanding Palisade Fence Rails and Posts
Palisade Fence Rails Overview
Palisade fences include two horizontal rails that provide crucial structural support. The exact specifications, such as the oversail distance from the center of the upper rail fixing to the top of the pales and from the center of the lower rail fixing to the bottom of the pales, appear in Table 2. This careful attention to detail ensures the fence aligns perfectly and is strongly built.
Palisade Fence Posts Details
You can install the posts for palisade fencing in two ways: embedding them in the earth or bolting them onto concrete foundations, depending on the specific site conditions and installation needs. For better security and design consistency, installers typically pair pointed top pales with similarly pointed posts. The standard spacing for posts is 2.75 meters, but installers can adjust this to meet specific site needs or preferences.
Types of Palisade Fence Posts
- RSJ Post: Known for its sturdy support, the RSJ post is ideal for high-security areas, particularly in industrial settings where strength is paramount.
- Square Post: Favored for its modern appearance, the square post is commonly used in commercial and residential areas where aesthetics are as important as security.
Fixing Methods for Palisade Fences
- Bolt Type: This method uses bolts to secure the fence components, allowing for easy adjustments or disassembly as needed.
- Embedded Type: This method involves embedding the posts directly into the ground for a permanent and stable installation. It is preferred in situations requiring enhanced stability.











 PF-08: Six types of corrugated pale head.
PF-08: Six types of corrugated pale head.
 PF-09: Five types of angle pales head.
PF-09: Five types of angle pales head.









